empowering the severely brain injured and their families via support, understanding and a network of care
Stroke leading to a Brain Injury
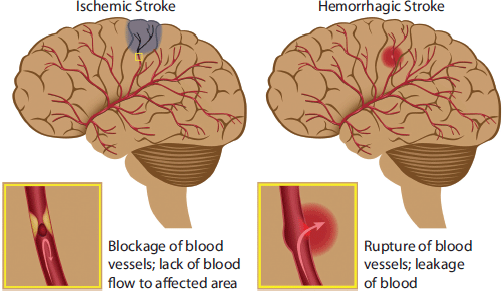
A Stroke is a disruption of blood supply to part of the brain that leads to a brain injury. There are two types of Stroke: Ischemic and Haemorrhagic.
What are the symptoms of a Stroke?
You often hear the expression ‘FAST’ used as an acronym for the symptoms of a Stroke.
F – face – Part of the face starts to droop, making it difficult to smile.
A – arms – The person is unable to fully lift their arms.
S – speech – The person has difficulties with speech, which becomes slurred.
T – time – It is time to call 999 and must be taken to hospital immediately.
Other symptoms that may occur are a sudden headache, confusion, dizziness, problems with communication or problems with vision.
How does a Stroke lead to a Brain Injury
As seen in the picture above there are a network of blood vessels that pump oxygen rich blood around the brain. This oxygen keeps the brain cells working and if this blood flow is disrupted by either a blood clot (Ischemic Stroke) or a burst blood vessel (Haemorrhagic Stroke), the brain cells are starved of oxygen and they begin to die. This would lead to a brain injury.
You may have heard of the term TIA which means Transient Ischemic Attack – these are mini strokes which occur when there is a temporary disruption to the blood supply to the brain due to a blocked blood vessel. The symptoms of a TIA are the same as a Stroke, but they only last for a few minutes or hours. Medical attention should be sought as soon as possible.
If you would like more information visit The Stroke Association web site.